Particles on the scale of hundreds of micrometres to nanometres are ubiquitous key components in many advanced applications including biomedical devices1,2, drug-delivery systems3,4,5,15, microelectronics12 and energy storage systems16,17, and exhibit inherent material applicability in microfluidics6,7, granular systems8,9 and abrasives14. Approaches to particle fabrication inherently have trade-offs among speed, scalability, geometric control, uniformity and material properties.
Traditional particle fabrication methods range from milling and emulsification techniques to advanced moulding and flow lithography, and approaches can be classified as either bottom-up or top-down. Bottom-up particle fabrication approaches, best exemplified by grinding and milling18, emulsification19, precipitation20, nucleation-and-growth21 and self-assembly5,10,11 techniques, can have high throughput but lead to heterogeneous populations of granular particles with limited control over shape and uniformity. To address the geometric shortcomings of bottom-up approaches, top-down particle fabrication methods such as direct lithography10,22, single-step roll-to-roll soft lithography23,24 and multistep moulding4 have been employed.
Scalable particle moulding approaches, such as particle replication in non-wetting templates (PRINT) and stamped assembly of polymer layers (SEAL), incorporate lithographic approaches to attain two-dimensional (2D) geometric control4,24. PRINT utilizes a non-wetting fluoropolymer layer to facilitate rapid fabrication of isolated micro- and nanoparticles with demonstratable precise control over shape, size, surface functionalization and fillers such as drugs, proteins or DNA/RNA24,25. Detailed in vitro studies of these particles have elucidated shape-dependent tendencies of cellular uptake and enhanced localized cargo release24,25,26. Moreover, in vivo studies have shown the significant role played by particle size, shape, charge, surface chemistry and particle deformability on biodistribution via multiple different dosage forms (injection and inhalation)27,28,29. Extending the PRINT technology, the stacking of moulded particles enables more complex particle geometries as exemplified by SEAL4. Harvested moulded sections are welded together to gain three-dimensional (3D) fabrication control, yielding demonstratable pulsatile-release, drug-delivery vehicles. The trajectory and demonstrated application potential of these technologies lays the groundwork for future methods of fabricating advanced particles.
For example, continuous-flow lithography (or optofluidic fabrication) produces particles as a photopolymerizable resin flows through a fluidic channel, curing in 2D to 3D geometries30,31. The stop-polymerize-flow technique has been demonstrated to achieve quasi-continuous fabrication of 2D to 2.5D geometries (anisotropic properties on a 2D-defined shape)32. Deterministic deformation based on microfluidic flow can further enable the fabrication of concave-surface geometries, previously demonstrated at the rate of 86,400 particles per day31. Furthermore, additional dimensional control processes may be introduced to create Janus particles (particles whose surfaces have two or more distinct physical properties), nanoporous meshes using sacrificial additives or porogens or micropatterning via secondary chemical coating or formation control steps2,33,34.
One remaining major engineering challenge is to develop a particle fabrication technique that simultaneously enables all dimensions of micron-scale 3D geometric control, complexity, speed, material selection and permutability. Herein we introduce a scalable, high-resolution 3D printing technique for particle fabrication based on a roll-to-roll form of continuous liquid interface production (r2rCLIP). We demonstrate r2rCLIP using single-digit, micron-resolution optics in combination with a continuous roll of film in lieu of a static platform, enabling fast, rapidly permutable fabrication and harvesting of particles with a variety of materials and complex geometries (Fig. 1).
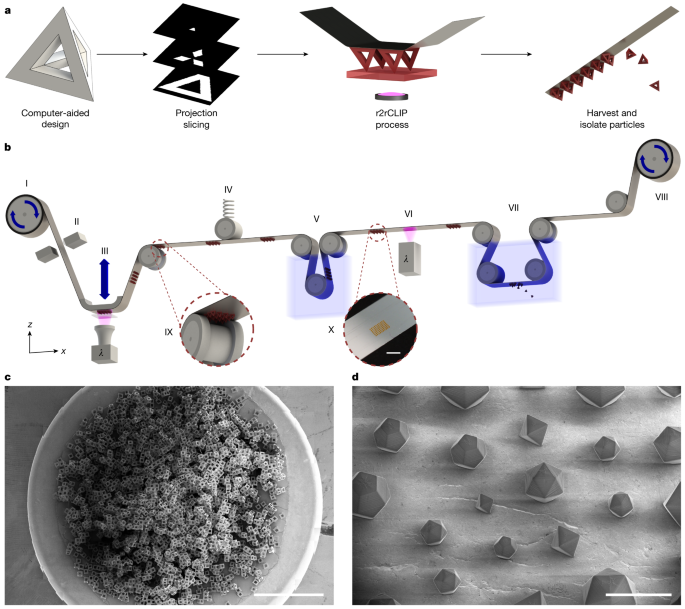
a, r2rCLIP is a quasi-continuous technique wherein a 3D geometry of simple to complex nature is designed and subsequently sliced into 2D images. These images are then used to fabricate 3D geometries from a photopolymerizable resin in a roll-to-roll process. b, Diagram of experimental r2rCLIP setup wherein an aluminium-coated PET film is unrolled from a feed roll (I) and mechanically braked (II) to provide tension before passing over a high-precision z stage and CLIP assembly (III). A designed geometry is projected through a Teflon AF window into a vat of photopolymerizable resin. The geometry materializes onto the film and the stage pulls in the z direction to direct vertical part formation. Once materialized, the particles on film are passed under a spring-tensioning system to maintain relative substrate positioning during stage movement (IV). The film is then passed through a cleaning step (V) before secondary curing (VI) and immersion in a non-ionic surfactant solution within a heated sonication bath and a razor blade to induce delamination (VII). The film is finally collected on a second roller with a stepper motor that provides translational movement throughout the process (VIII; Extended Data Fig. 1). Insets show a graphic of particle clearance over a guide roller (IX) and an image of particles on the film post cleaning (X). c, This scalable process is demonstrated by the production of around 30,000 hollow cube particles observed in a set of computer-stitched scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images. d, Octahedrons, icosahedrons and dodecahedrons with unit cell size ranging from 200 to 400 µm printed within a singular printed array. c,d, Samples printed from the HDDA–HDDMA system and coated with Au/Pd (60:40) before SEM imaging. Scale bars, 3 mm (b,c), 500 µm (d).
Continuous liquid interface production is an additive manufacturing technique that uses digital light processing (DLP) to project videos of 2D images describing 3D models into a vat of photopolymerizable resin. The resolution of this technique has improved from 50 to 4.5 μm, as well as providing speeds of up to 3,000 mm h−1 (refs. 35,36,37,38). CLIP utilizes a 385 nm ultraviolet light-emitting diode (LED) and digital micromirror device to simultaneously pattern an array of actinic photons, activating photo-initiators dissolved in liquid resin and inducing radical polymerization in each printed voxel. The CLIP technique is distinguished by the introduction of an oxygen-induced, photopolymerization-inhibited ‘dead zone’ between the photocurable resin and an optically clear vat window (Teflon amorphous fluoropolymer (AF) 1600 or 2400), effectively obviating any delamination step (Extended Data Fig. 2. and Supplementary Note 1). Lack of adherence, or glueing, of the growing particle onto the window facilitates fabrication of fragile green parts, such as thin struts on hollowed particle geometries, while maintaining high throughput speeds35,36. This technique is demonstrably versatile for a broad range of polymer chemistries, functionalization, fillers and multimaterial platforms35,38. High-resolution CLIP is used herein to obtain geometric control for the scalable fabrication of particles in the sub-200-µm regime with resin-dependent, layer-wise control down to single-digit-micron range and 2.00 × 2.00 µm2 xy resolution.
To achieve a rapid and fully automated particle-printing process we substituted the conventional static build plate of a high-resolution CLIP printer with a continuous-film, modular, roll-to-roll system. This enables semicontinuous printing and automated in-line postprocessing including cleaning, postcuring and harvesting (particle liftoff). An aluminium-coated polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film was chosen as the primary film substrate to maintain particle adhesion during printing at a level above in situ orthogonal resin reflow forces and normal suction forces, still allowing for delamination from film without fracture during harvesting (for additional substrates tested see Supplementary Note 2).
Complementary to film integration for particle printing, we constructed a high-resolution CLIP setup to fabricate fine particle features that achieves single-digit-micron optical resolution (2.00 × 2.00 or 6.00 × 6.00 µm2 depending on desired build area) in the xy plane. Voxel definition further depends on vertical resolution, dependent on stage movement repeatability (±0.12 μm), depth of focus of the optical setup (for example, 30 μm for 2.00 × 2.00 µm2 setup) and resin physical properties (refraction and diffraction of light, penetration depth and critical exposure dose for gelation; Table 1, Fig. 2 and Supplementary Note 3).
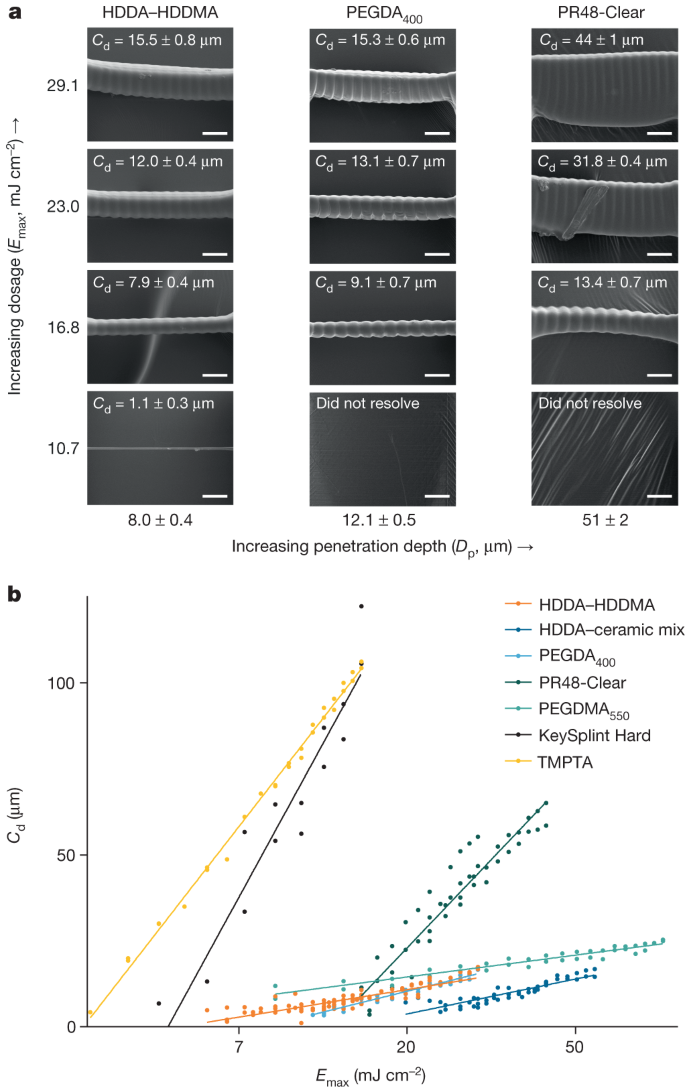
a, The bridging method enables working curve determination of resin-curing properties, as demonstrated for several bridge series from resins of increasing penetration depth at constant dosage and corresponding measured cure depth. Ridging artefacts coincide with pixel pitch at 6 µm spacing. Exposure measurement bridges coated with Au/Pd (60:40) before SEM imaging. b, Determination of intrinsic penetration depth and critical cure dosage. A lower slope correlates with greater analytical cure depth control at a given dosage (Emax), as well as with a lower propensity for fluctuations in exposure to result in major changes in cure depth (Cd). Scale bars, 15 µm.
Source Data
Previous work has studied surface and resolution optimization in photopolymerization-based 3D printing systems39; achieving z resolution below 25 µm remains a challenge due to intrinsic resin penetration depth and overcuring from accumulated dosages40,41,42. To fabricate optimal, complex particle geometries a resin system must be designed to achieve high z resolution; a 1,6-hexanediol diacrylate–1,6-hexanediol dimethacrylate (HDDA–HDDMA)-based system was previously described as achieving up to 4 µm vertical resolution39. We utilize this resin system herein and adopt an analytical bridging technique to measure intrinsic resin properties, as opposed to the common glass slide method40,42,43 which does not analytically describe in situ high-resolution CLIP as accurately. Our HDDA–HDDMA resin has a characteristic penetration depth of 8.0 ± 0.4 µm and experimentally resolved a minimum unsupported bridge thickness of 1.1 ± 0.3 µm. We characterized several additional high-resolution custom and commercial resin compositions, which are also compatible with r2rCLIP and may be substituted depending on materials requirements, desired vertical resolution and application (Table 1 and Fig. 2). Notably, unsupported film bridges characterized in the curing assay are thin (under 100 µm, relevant to particle fabrication) and resolve proximal to the dead zone, introducing periodic artefacts ascribed to fluctuations in light intensity between pixels. Surface irregularities may further be attributed to either resin reflow (elongated lines) or cavitation (bubbles) and may be addressed with optimization. Resin parameterization and optimization are essential in regard to vertical resolution determination for fabrication limitations; resins with greater characteristic penetration depth are not as amenable to thin vertical geometric features.
To demonstrate the potential of r2rCLIP in the fabrication of dimensionally complex structures we designed a range of shapes with increasing geometric complexity using computer-aided design. These designs not only mirror those created by previous 2D fabrication and multistep moulding techniques4,24 but also include several geometries that cannot be moulded, exemplifying the unique capabilities of our approach (Fig. 3). Herein we categorize geometric complexity on a spectrum ranging from shapes that can be moulded at scale to those that cannot. Mouldable geometries are defined to be plausibly fabricated at scale in a single step using a uniaxial die draw, core and cavity. Geometries increase in moulding complexity (and subsequently decrease in mouldability at scale) if a theoretical moulding approach requires an increasing number of parting lines, ejector pins and angles and extensive alignment or contains non-mouldable negative internal spaces. In addition, thin or sharp geometric features may introduce moulding complications and part anisotropy due to, for example, flash, short shot, shrinkage or air pockets exacerbated at the micron scale (Supplementary Note 4)44. It should be noted that it is plausible to couple a multistep moulding process with a sacrificial etching step to achieve some geometries deemed non-mouldable in this work, although without a high degree of reproducibility given mould alignment requirements.
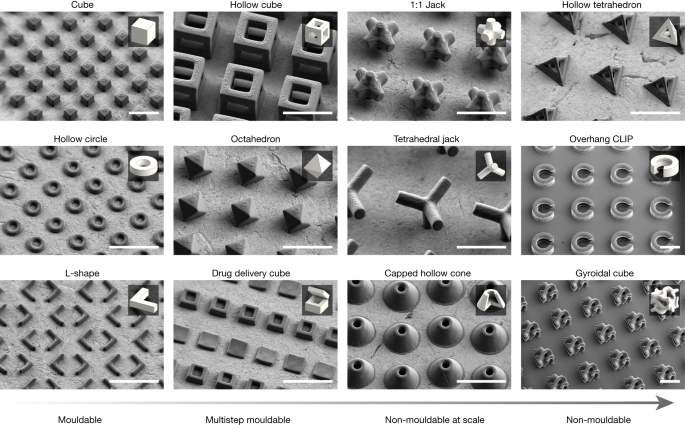
Particles were fabricated using the HDDA–HDDMA system and informed exposure intensities obtained from bridge fitting data (Fig. 2 and Table 1), washed as described and coated with a 60:40 Au/Pd before SEM observation. Insets show a rendering of each respective geometry for reference. Capped hollow cone inset shown as quarter cut-through for clarity. Scale bars, 250 µm.
One significant benefit of using the r2rCLIP method for particle fabrication is its inherent mouldless process, which enables changing of fabricated geometries within or between arrays based solely on optimized printing parameters. This means that a wide variety of particle geometries can be produced without needing to alter the setup, as would be necessary with previous particle fabrication methods (for example, mould interchange). This flexibility is particularly beneficial when needing to adjust geometric requirements, such as when fabricating precise ratios of heterogeneous mixtures of polydisperse particles (Fig. 1d).
To demonstrate the scalability afforded by r2rCLIP we fabricated approximately 30,000 hollow cube-shaped particles of 200 µm width and high reproducibility (Fig. 1c; 96 ± 1% fabrication success rate, n = 300; −10 ± 20% average relative error from nominal strut feature size, n = 300). Whereas optimized particle array (up to 16.4 mm2 for 2 µm or 147.5 mm2 for 6 µm resolution) fabrication speed is subminute, gram-scale production (thousands to millions of particles) necessitates the removal of time-consuming, manual manipulation steps. Previously the slow step of particle production involved the manual replacement of build substrate (requiring 4 ± 2 min for manual manipulation between high-resolution CLIP print jobs, n = 6,436; Supplementary Note 5). Replacing this manual manipulation step with mechanical substrate translation shifts the rate-limiting step to particle fabrication time—an inherent advantage of the r2rCLIP technique. For instance, fabrication of 1 million 200-µm-unit octahedrons (equal to approximately 1.4 g) would require just over 1 day with demonstrated array fabrication speeds of up to 38 s print duration with 26 s interprint delay (Supplementary Note 6). The r2rCLIP platform thus enables a new design application of particle fabrication in a wide range of accessible geometries, materials and batch sizes. r2rCLIP is a modular process that can thus be adapted to include additional steps in series such as coating, filling or sterilization, as well as additional postharvesting treatments such as devolatilization, electroless deposition or functionalization. The high throughput of r2rCLIP has direct implications for industrial-scale production of microdevices such as microrobots and cargo delivery systems.
As an example, this system is amenable to the production of ceramic materials. Preceramic resins can be used to mass produce technical ceramic particles, with potential applications in chemical mechanical planarization techniques as slurry components, conductive particles, in microtools, microelectromechanical systems or waveguides, enabling industrial applications such as electronics, telecommunications and healthcare13. As an example, we created 200 µm particles from a HDDA–preceramic mix and pyrolysed them in nitrogen at 800 °C to produce 103 µm hollow ceramic particles of feature size 25 µm (Fig. 4a). Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analysis of these particles showed uniform composition distribution of O, Si and C (Fig. 4b). With subsequent annealing up to 1,400 °C in nitrogen, phases including Si3N4 and SiO2 can be achieved depending on the precursor material and processing conditions (Extended Data Fig. 3 and Supplementary Note 7). Future research can investigate the effectiveness of this process with different preceramic formulations and explore their potential applications.
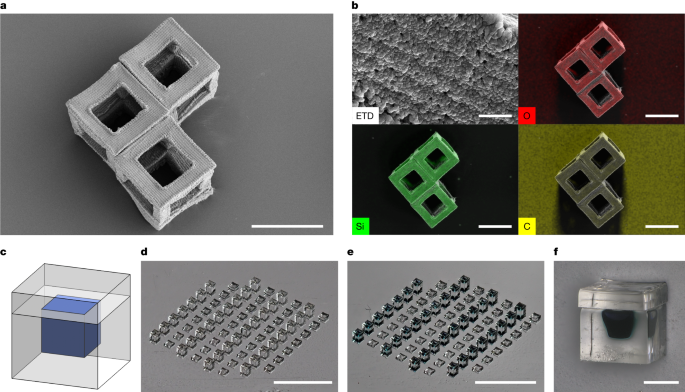
a, Hollow ceramic cubes formed from pyrolysis of HDDA–ceramic mix resin. b, EDS analysis of the surface of a hollow ceramic cube (top left) showing uniform distribution of silicon and oxygen, quantified as 30 ± 1% silicon, 35 ± 1% oxygen and 35 ± 2% carbon by normalized mass. Elemental distribution of O, Si and C (top right, bottom left and bottom right, respectively) overlaid on secondary electron image of the hollow cubes. c,d, Drug-delivery cubes may be designed to meet the goals of payload volume, release profile, material and so on (c) and fabricated via r2rCLIP (d) (PEGDMA550 material, for example). e,f, Devices may be then filled, as demonstrated with trypan blue dye for visualization (e), and subsequently capped (f). Scale bars, 100 µm (a), 5 µm (b, top left), 100 µm (b, other three images), 3 mm (d,e), 200 µm (f).
One further application enabled by r2rCLIP is the creation of hydrogel particles, which can be used as drug-delivery vessels. These particles can be filled to achieve adjustable, gradient or pulsatile-release profiles in a singular injection, as previously demonstrated for the SEAL process4,45,46. Previous studies have explored the development of suitable photopolymer resin systems and the impact of materials biocompatibility, cytotoxicity, shape and size on localization and delivery, enabling the creation of bioscaffolds and delivery manifolds5,15,23,25,28,45,46,47,48,49. This opens new possibilities for the fabrication of hydrogel particles for drug delivery but lacks a permutable, scalable fabrication process. As a proof of concept we have fabricated hydrogel cubes of 400 µm unit size, manually filled with around 8 nl of representative cargo postprinting and subsequently topped with a hydrogel cap (Fig. 4c). Future research can build on previous studies on drug-delivery vehicle kinetics, leveraging the adjustable properties of molecular weight and wall thickness to achieve a programmable pallet of cargo release.
Furthermore, amine-functionalized polymer end groups could be added to facilitate postfunctionalization with fluorophores, enabling the potential to integrate single-particle, one-pot analytical techniques to localize signal for better detection. Smaller unit scale geometries and additional materials such as metals may even be achieved through thermal conversion postprocessing that could lead to roughly 70% reduction in feature size50, which would bring our current xy resolution onto the nanometre scale. Future system improvement work can explore print and speed optimization, soluble film coatings, cleaning and particle-harvesting methods.
The mechanical and material versatility, ranging from hard ceramics to soft hydrogels, could support the creation of Janus particle properties and smart materials and aid in fundamental studies in materials and granular physics. Although the system requires a photopolymerizable component, it can accommodate weak, green-state particles enabling mixed, dual-curing systems containing a non-photopolymerizable component addressed in postprocessing. This flexibility allows for tunable particle materials properties dependent on the resin system, enabling a variety of particles with different mechanical properties to meet application requirements.
Herein we present a new, roll-to-roll, high-resolution, continuous liquid interface production technique capable of mass production of particles up to 200 µm at up to 2.0 µm feature resolution. Optical design of both printer and resin optimization enables printing of objects with up to single-digit-micron unsupported z resolution. Rapid permutability, complex 3D fabrication capabilities and inherent amenability to a wide variety of resin chemistries are demonstrated in the fabrication of mouldable, multistep mouldable and non-mouldable particle geometries. Moreover, rapid particle production enables gram-scale potential yield within a period of around 24 h for sub-200-µm units. This scalable particle production technique has demonstrated fabrication potential over a wide range, from ceramic to hydrogel manifolds, with subsequent potential application in microtools, electronics and drug delivery.
