Hello Nature readers, would you like to get this Briefing in your inbox free every day? Sign up here

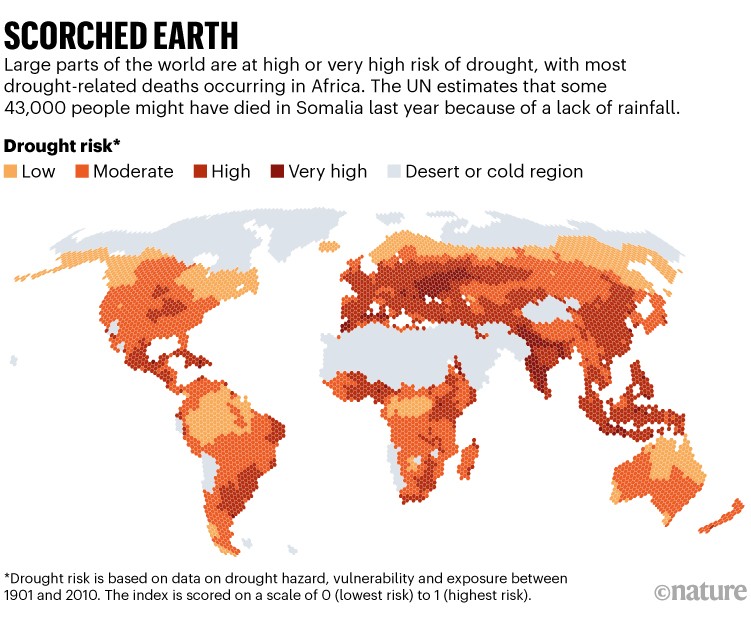
As many as 43,000 people might have died as a result of drought in Somalia last year, according to a report published this week by the Somalian government, the UN children’s agency UNICEF and the World Health Organization.Credit: Jerome Delay/AP/Shutterstock
The United Nations (UN) water conference currently taking place in New York is the first meeting in nearly half a century that focuses on access to safe water for the hundreds of millions of people that lack it. The water crisis is worst in low-income countries. In sub-Saharan Africa, it’s estimated that 70% of the population does not have basic water services — and more people there lack water now than 20 years ago. A target set in 2015 to provide clean water and sanitation to all by 2030 is likely to be missed if the current slow rates of improvement continue. The conference will produce a water action agenda, although unlike the Paris climate agreement, it won’t include binding commitments.
Nature | 6 min read
Fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) have surprised researchers with an entirely new taste receptor that allows them to detect alkaline — or basic — substances and avoid toxic meals and surfaces. The flies have an unusual mechanism: a receptor protein that, in the presence of a base, opens a cell-membrane channel through which negatively charged chloride ions escape the neuron. Most sensory receptors involve channels that let positively charged ions flow into the cell. Some studies in people and cats suggest that they, too, experience alkaline as a type of taste.
Nature | 4 min read
Reference: Nature Metabolism paper
How many people do you have to invite to a party to ensure that any given number of them are all friends, or all strangers? The best upper limit for this surprisingly hard problem, which has plagued mathematicians for almost 100 years, is (3.9995)k, with k being the size of the group of either all friends or all strangers. Until now, the best answer had been ‘at most 4k’, calculated in 1935. Even lowering the upper limit by this tiny amount is “a stunning success”, says combinatorialist David Conlon. The result is important for studying networks that have an element of randomness, which can crop up in real-world scenarios ranging from epidemiology to optimization and scheduling problems.
Nature | 5 min read
Reference: arXiv preprint (not peer reviewed)
DNA extracted from 200-year-old locks of Ludwig van Beethoven’s hair has given geneticists clues about why the composer died: he was particularly susceptible to liver disease. Beethoven also had viral hepatitis in the months before his death — and historical reports suggest he was a heavy drinker. The cause of Beethoven’s hearing loss, which affected the composer for most of his later life, remains a mystery.
Nature | 5 min read
Reference: Current Biology paper
Features & opinion
Table of Contents
Many researchers complain about excessive detail in colleagues’ talks but fail to address the issue in their own, writes David Rubenson, director of a scientific communications firm. He recommends taking four steps to create clearer, more-concise presentations:
• Write your points down in a smooth, half-page narrative.
• Read your narrative to a scientist in your field and another outside it.
• Create slides for a 5-minute presentation, then keep adding to it.
• For each slide, start with a title and the minimum amount of information, and build them up from there.
Nature | 5 min read
The Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) aims to shake up the conventional model of funding biomedical research — which some deem too slow and conservative. Armed with a US$2.5-billion budget, the agency will focus on high-risk, high-reward projects. “We really want to see boldness,” says ARPA-H director Renee Wegrzyn, as she shares her advice for scientists who want to apply.
Nature | 5 min read
In 1949, physicist Chien-Shiung Wu documented the first evidence of a strange quantum phenomenon called entanglement. Last year, work on entanglement starting in the 1970s gained Alain Aspect, John Clauser and Anton Zeilinger the physics Nobel prize. Wu, who died in 1997, was not mentioned during the award announcement — and it’s not the first time she has been overlooked. In 1957, Wu’s experiments toppled the physics principle of parity. Despite backlash from the physics community, it was her colleagues Chen Ning Yang and Tsung-Dao Lee who received the physics Nobel prize for the achievement.
Scientific American | 14 min read
Source: IPCC
Around half of the world’s population is at risk of severe water scarcity for at least some of the year. The impact of climate change is likely to increase this number. If global temperatures reach 1.5 °C above pre-industrial temperatures, extreme soil moisture drought is expected to be twice as likely in many parts of the world. (Source: IPCC)
